Permeability of package material is one of the main factors in determining the application fields and content material quality. Since gases such as oxygen and carbon dioxide permeating through the package will exert obvious influences on product quality, material with proper permeability should be selected while taking the guarantee period of precuts into consideration in design of package. Gas permeability instrument is one of the advanced testing instruments that have been selected and purchased by package manufacturers and users in recent years.
1. Development of Gas Permeability Testing
Gas permeability testing, as one of the main permeability indexes of materials, is also called gas permeation testing or gas transmission testing. It is mainly used for the permeability investigation of film and sheet for common inorganic gases. Oxygen permeability is the commonly tested object. Since the wide application of modified air package, carbon dioxide and nitrogen permeability of package materials need to be tested as well.
Auto gas permeability testing can be divided into differential-pressure method and equal-pressure method. The most widely used is differential pressure method, which includes vacuum differential pressure method and volume method. With the development of oxygen micro detection, micro oxygen sensor is gradually used in the field of oxygen permeability of material, i.e., sensor method of gas permeability testing. Different gas sensors can be used to test the permeability of different gases. At present, testing technologies of oxygen and carbon dioxide permeability have been mature already. Gas permeability can also be tested using gas chromatography method, which belongs to equal pressure method of auto gas permeability testing in addition to sensor method.
2. Differential Pressure Method

Fig.1. Testing Principle of Vacuum Method
Vacuum method is the most representative one of differential pressure method. In this method, (see fig 1) the permeation cavity is divided into two independent parts by the specimen. Vacuate the two sides and then fill one side (side A, the high pressure side) with testing gas of 0.1Mpa (absolute pressure) and the other side keeps the vacuum state. Testing gas between the two sides will form a pressure difference of 0.1Mpa. The testing gas transmits through the film into the low-pressure side and causes a pressure change there. According to the formula, gas transmission rate (GTR) can be calculated with the pressure variation measured by the high precision vacuum gauge. Relating standard are ISO 2556, ISO 15105-1, ASTM D 1434 (M method), GB 1038, JIS K 7126 (A method) and so on. GTR calculation formula offered by standard ISO 15105-1 is as below:

Vc represents the volume of low-pressure side;
T is the test temperature (thermodynamic temperature);
A is the effective transmission area;
dp/dt is the pressure variation on low pressure side per unit time after the transmission has become stable.
R is the gas constant.
In vacuum process, the pressure difference of 0.1Mpa between the two sides is realized with negative pressure difference principle. There is no doubt that the principle of positive pressure difference, usually volume method, can also be used. By volume method, there is no need to evacuate the cavity and keep the vacuum status. Therefore, it reduces the difficulty of instrument manufacturing and permeation test. Relating standard is ASTM D 1434 (V method).
Differential pressure method has a good universality for testing gases. With the theoretical support of film technology, vacuum method has been used as the basic method in gas permeability testing and it is adopted by most of the scientific research institutions. As the testing technology of vacuum gauge is developing and with the application of advanced vacuum technology in instrument designing, testing accuracy and data repeatability have been greatly improved. The outstanding merit of this method is that the three permeability indexes –permeability coefficient, diffusion coefficient and solubility coefficient –can be obtained through one testing.
When selecting and purchasing gas permeability instrument of vacuum differential pressure method, attentions should be paid to the following parameter indexes: vacuum degree to be reached, precision & range of vacuum gauges, blank test data & repeatability of testing data and the self temperature control function of instruments. Vacuum degree of testing chamber not only signifies vacuumizing ability of the adopted vacuum pump, it also represents the sealing property of cavity body and relevant pipeline. If there is leaking points in the mechanical structure, testing results will be seriously influenced and consequently actual permeability of material cannot be expressed. If requirement of vacuum degree of certain testing cannot be satisfied, the cause may be the improper sealing of specimen attachment. Standard requirement for the precision of vacuum gauge is no less than 6Pa. The resolution of excellent vacuum gauge is 0.1 % of its full measuring range at present. Since resolution of testing components is superior to its testing precision, measuring range of vacuum gauge is usually less than 6Kpa. ‘Blank test ' data and testing repeatability of the data are the comprehensive indexes in judging instruments under the influences of various factors. The controlling of temperature and humidity of testing environment, especially temperature controlling, will also exert influences on testing results. Detailed information about the influence can refer to the articles updated on January 17, 2005 and February 21 in Labthink Lab Forum. When selecting and purchasing positive differential pressure instrument, since vacuumization is not needed in this method, we can pay attention only to indexes of precision, measuring range, data of blank test and testing data repeatability of pressure sensor.
3. Equal Pressure Method
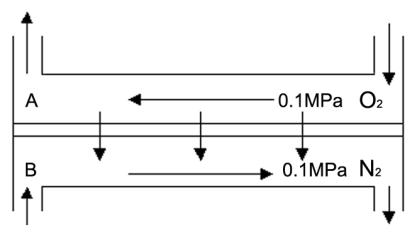
Fig.2. Testing Principle of Sensor Method
Sensor testing is the main method presently used in equal pressure method of gas permeability testing. It is mainly used for oxygen permeation testing. The testing principle is (see fig 2): use the specimen to divide the permeation cavity into two independent airflow systems with one side as the flowing testing gas (A, pure oxygen or mixed gas with oxygen) and the other side as the flowing dry nitrogen gas (B). The pressures of the two sides are equal but oxygen partial pressure is different. Under the function of oxygen concentration difference, oxygen transits through the film and is delivered to the sensor by nitrogen carrier gas. Oxygen gas transmission rate (O2GTR) of the package can be calculated through the oxygen quantity that is precisely measured by the sensor in nitrogen carrier gas. Sensor method instruments should be calibrated with reference film before formal testing, with an aim to determine the calibrate factor and used it in the formal testing calculation. Relating standards about sensor method are ISO 15105-2, ASTM D 3985, ASTM F 1927, ASTM F 1307 and so on. Calculation formula of O2GTR offered by ISO 15105-2 is as below:

Where:
U is the output signal of zero voltage in testing;
U0 is the signal for zero voltage;
K is the calibration factor;
pa is the environment atmospheric pressure;
p0 is the oxygen partial pressure in testing gas;
A is the effective transmission area.
Oxygen sensor is used in oxygen permeability testing of material and can only perform permeability analysis of oxygen gas. For the reason that nitrogen gas is used as carrier gas to transport testing gas through specimen, its permeability cannot be tested with such kind of testing structure at present.
The sensor testing method appears as oxygen detector technology has been constantly maturing. Comparing with vacuum method, testing time of sensor method is shortened; and it is used in the testing of high permeability materials more frequently. Corrected factors of the instrument are not always effective and need to be periodically calibrated as required because the sensor used belongs to the consuming type. And the sensor must be changed when it has deteriorated to a certain extend. This made testing cost of sensor method instrument a little higher than that of differential pressure testers. Sensors of different manufacturers have different service lives. In normal condition, the oxygen sensor of Labthink TOY-C1 has a service life of 12 to 30 months, which is relatively long. In equal pressure method, both sides of the specimen remain normal atmosphere to make the two sides an equal pressure. This also establishes a basis for the testing of container package oxygen permeability testing, during which package burst resulting from big pressure difference existing between two sides can be avoid. ASTM F 1307 is the standard of package oxygen permeability testing. Design of instrument structure and operation method of oxygen sensor in this standard is similar to that of standard ASTM D 3985 (testing oxygen permeability of film and sheet). When package testing accessories are removed, the same instrument can well complete film and sheet oxygen permeability testing according to standard ASTM D 3985. At present, instruments that possess dual operation of both film and package oxygen permeability testing are already in the market, among that Labthink TOY-C1 package /film oxygen permeability tester is an example.
4. Selection of Testing Instrument
For differential pressure method and equal pressure method, the test principle and test condition are different. The result units are also different from each other (the unit of differential pressure method is cm3/m2·24h·0.1Mpa and that of equal pressure method is cm3/m2·d). Theoretically speaking there is no comparability between the uncalibrated data obtained from the two methods. But, the comparison of testing results of differential pressure method and equal pressure method become possible after calibrating the instrument of equal pressure method with reference film and using that corrected factor in the formal testing.
In our country, market share of differential pressure method instruments is a lot higher than that of equal pressure method. This is partially because only differential pressure method is employed in gas permeability in domestic standards, and partially related with the profound foundation of differential pressure theory. In European and <st1:country-region w:st="on">Japan, although both methods are recognized, differential pressure method gains more favor in institutions of scientific research and testing.
Sometimes, when selecting and purchasing gas permeability instruments, customers are unable to decide which instruments are closer to their actual testing purpose. The following advices are offered with a hope to provide some help for the would-be purchasers. First, research institutions often choose vacuum differential pressure instrument, which can test the coefficients of permeability, diffusion and solubility simultaneously, which has certain directive significance for the study of material permeability. Second, differential pressure method has a good versatility for testing gas.
Secondly, for gas-filled and modified air package, the actual environment of package material is closer to that of the equal pressure-testing. However, vacuum differential pressure method is more suitable for vacuum package material due to the environment similarity of vacuum package material and vacuum differential pressure method. Concentricity of testing objects and testing frequency should also be taken into consideration. Thirdly, if there is only one testing item (such as oxygen permeability testing only) and the testing frequency is not high, equal pressure oxygen permeability tester can be considered. Otherwise differential pressure instruments should be adopted. If testing frequency is high, differential pressure instruments can also be applied, this is because equal pressure sensor is of consumable kind. The more frequent the testing tasks, the shorter its life span. Due to the high cost of sensor replacement, testing cost of differential pressure instrument is some lower.
